Statutory Compliance in HR and Payroll in India: Complete Guide
Every company in India spends a lot of money, effort and time to ensure that its payroll is compliant through a proper audit. Companies often worry about facing legal issues that are related to compliance such as aggressive employees, demands of unreasonable wage, and demands from trade unions. Even if a company doesn’t have any intention to break laws, it may face legal troubles if it doesn’t have proper protection. This protection comes in the form of statutory compliance which helps the companies to avoid the risk of non-compliance. With increasing non-compliance risks, it becomes necessary for the companies in India to have statutory compliance in HR in India.
What is Statutory Compliance in HR?
Statutory compliance is the most discussed term; Statutory means “related to statutes,” which is Rules and Regulations. Compliance stands for adherence. Thus Statutory compliance means “To Follow the rules and regulations.”
Statutory compliance is a legal framework under which the Company must function all its duties. Firstly, every organization must treat its employees to follow all central & state labor laws.
All these laws secure the welfare of the Company, employee, and employer. Therefore, regardless of its size, every organization needs to follow the central and state labor laws. And if any organization fails to adhere, strict legal action can be taken against them.
“Latest Update on Statutory”: Zomato and Swiggy now pay TCS to the Government Instead of the Restaurant.
Zomato, Swiggy, and all food delivery apps are registered as Tax Collected at Source (TCS) in GST records. Revenue secretary Tarun Bajaj quoted – ” This move will not impact the end consumer in any way, as there is no extra tax to be paid. Restaurants previously paid the Tax, and now it will be paid by the aggregators; this will help protect the revenue leakage.”
Most frequently used food delivery apps like Zomato and Swiggy will now be liable to pay 5% Goods and Services Tax (GST) on orders collected from the ultimate consumer, which in the present regime is paid by the restaurants they pick orders from. Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman stated this in a meeting of the 45th GST Council held in Lucknow.
This law would come into effect from January 1, 2022, to allow the e-commerce operators to make the necessary changes in their respected software for the operations.
According to the reports, the revenue leakage due to alleged under-reporting by food delivery apps was around Rs 2000 Cr in the last two years. This will ensure effective implementation of GST, and the Government will gain around 5000 Cr – 7000 Cr with the change in this collection system in the next 4-5 years.
The step was taken because Zomato/Swiggy held no mandatory registration check, and there were plenty of unregistered restaurants delivering using the Apps. This would help protect the revenue leak and get the Government to conquer the bribery in the system.
The most significant benefits of this Amendment, as discussed in the 45th GST Council Meeting, are:
1. It will cut down the intermediaries between the Government and the aggregators, which will lead to less corruption in the process.
2. As there would be only 2 parties involved in this transaction, the Government & Aggregator, there would be more accountability, transparency, and easy tracking.
3. Transparency in implementation will generate greater revenue by filling all the gaps prevalent in the system, which led to a lot of revenue leakage.
4. The icing on the cake is, increase the revenue without leading any extra tax burden on the ultimate customer.
Conclusion:
There was never an issue with the taxation laws in India; the issue was always the ineffective implementation. Therefore, the implementation of this law will be a stepping stone and a positive stride towards a more effective and efficient taxation system in which the Government will get its fair share and ultimately divert those funds towards the betterment of the nation as a whole.
Importance of Statutory Compliance in Payroll?
Every country owns its own set of state and indian labor laws, which every company needs to follow. To deal with statutory compliance, it requires the companies to be updated on all labor regulations in their country. In addition, it is mandated for the companies to follow all the laws and regulations. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead the Company to face many legal issues, including fines and penalties.
This is the very reason a company puts a tremendous amount of money, time, and effort into meeting the compliance requirements right from professional tax to minimum wages Act. To match with all the demanding regulatory environments, every organization should be well updated and keep an eye on all the regulations in the labor laws.
Statutory compliance is something that is beneficial to everyone- Employees, employers,s and the whole Company.
1. Work stoppage
2. Loss of the company’s integrity, reputation, and goodwill
3. Cancellation and suspension of operational licenses
4. Loss of faith in the company’s stakeholders and investors
5. Imposition of fines
6. Loss of customer loyalty
7. Civil and criminal liabilities
8. Negative impact on the company’s productivity
9. Penal liabilities against the Directors or officers of the company
10. Withdrawal of fiscal benefits
11. A shutdown of the company, if the case goes on an extreme level.
Statutory compliance in HR helps a company to manage a demanding regulatory environment and avoid non-compliance risks.
All the labour and taxation laws of India come under statutory compliance. Every company in India has to mandatorily obey these laws which change on a National and State level. If a company is non-compliant with these regulations, it can face legal troubles like fines, penalties or even complete shutdown. To avoid such risks, a company should spend a good amount of resources to ensure statutory compliance in HR. Companies must understand all the labour and taxation laws of India to stay updated about any changes they need to incorporate in their organizations. The rules keep evolving from time to time, and the laws are quite dynamic.
The following Labour Acts in India require statutory compliance:
1. The Child Labour (Prohibition & Regulation Act), 1986
2. Inter-State Migrant Workmen( Regulation Of Employment & Conditions Of Service ) Act, 1979
3. The Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
4. The Payment Of Gratuity Act, 1972
5. The Contract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) Act, 1970
6. The Payment Of Bonus Act, 1965
7. The Apprentices Act, 1961
8. The Employment Exchanges(Compulsory Notification Of Vacancies) Act, 1959
9. The Employees Provident Fund & Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952
10. The Factories Act, 1948
11. The Minimum Wages Act, 1948
12. The Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948
13. The Industrial Disputes Act of 1946
14. The Industrial Employment Standing Orders Act, 1946
15. The Payment Of Wages Act, 1936
16. The Trade Unions Act, 1926
17. The Workmen’s Compensation Act, 1923
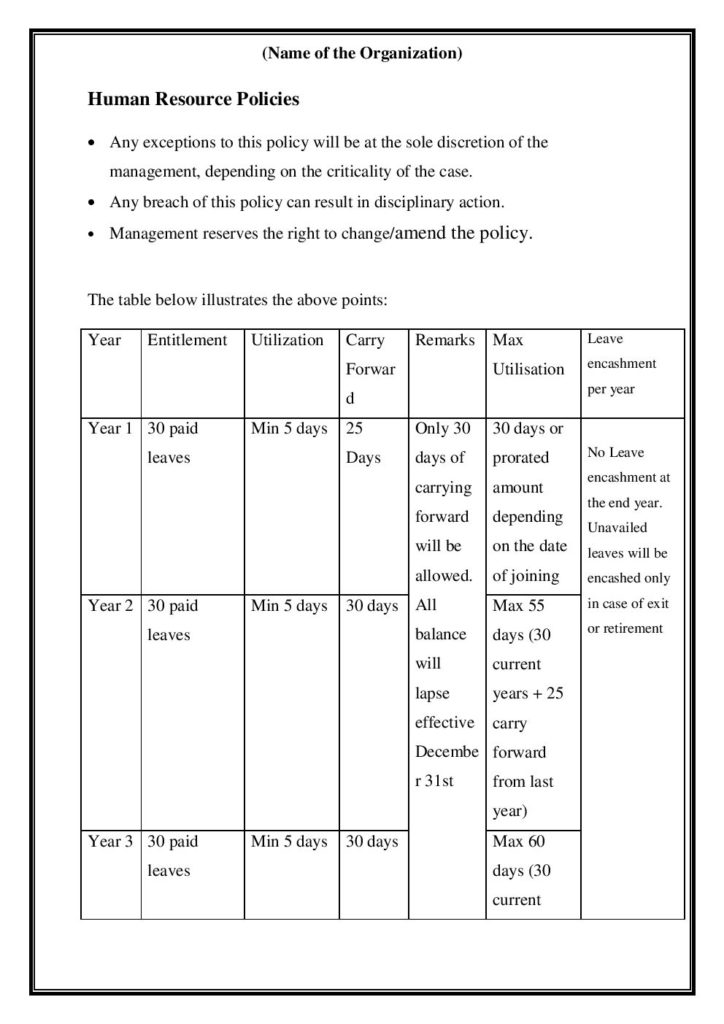
Minimum Wages Act, 1948
The Minimum wages Act fixes the minimum wage rates in any Indian company, where both the Provincial Government and the Central Government determine these rates. The minimum wage rates get declared at the occupational, sectoral, state, and national levels. These wages may get established for any sector, occupation, or region. The cost of living determines the minimum wage. The minimum wages may get set for different scheduled employment or various work classes of the same scheduled employment. The frequency of the salaries ranges from monthly, hourly, or daily. The State Government and Central Government notify the scheduled employment about revising minimum wage rates.
The two methods for fixing or revising minimum wages are:
1. Committee method
In this method, the government changes minimum wages after setting up committees and subcommittees to hold recommendations and inquiries.
2. Notification method
In this method, the Official Gazette publishes proposals of the government regarding people who are likely to be affected by changes in minimum wages. The recommendations get taken into consideration at a specified date.
The government fixes or revises the minimum wage of particular scheduled employment after considering all the representations and committees’ advice. The final decision gets implemented after 3 months from the date of its declaration.
Payment of Bonus Act,1965
The Indian Government efficiently makes payment of Bonus Act,1965 to ensure that the employees receive a decent share of the profit made by the organization; the Payment of Bonus Act provides an annual bonus to every employee present in the Company. This Act applies to all factories, including 20 or more employees.
The bonus is calculated based on the employee’s salary, performance, and profits earned by the Company. The main aim of this enactment is to lay down a legal obligation on the employer to provide for the bonus payment.
An Employee earning ₹21,000/- or less, removing other allowances, and who has worked for more than 30 days with the organization is eligible to claim this bonus.
As per the 2015 Amendment, the Ceiling amount of Rs 7000 (max) is the salary to calculate the bonus. And the % for the bonus would be around 8.33%, min to max 20% under section 10 of the Act.
List of Statutory Compliance in HR – by StartupHR Toolkit
1. Introduction to Statutory
2. Payment of Wages Act, 1936
3. Minimum Wages Act, 1948
4. The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
5. Tax Deduction at Source (TDS)
6. Professional Tax
7. Amendments to Maternity Benefit Act, 1961
8. Equal Remuneration Act, 1976
9. Shops & Establishments Act
10. The Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948 (ESIC)
11. The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
12. Employees Provident Fund (PF) and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952
13. Labour Welfare Fund Act, 1965
14. Labour Law Annual Leave and Holidays
15. Labour Law Compensation
16. Labour law Fair Treatment
17. Labour law health and safety
18. Labour Law Trade Union
Need for Statutory Compliance in HR in India?
It has become more complicated to do business in India. Companies in India also face the challenge of going hand in hand with the operational aspect of its core business. All the companies operating in India have to ensure the following categories of statutory regulations and mandates:
1) Employment laws
2) Tax laws
3) Labour laws
4) Competition and antitrust laws
5) Environmental regulations
6) Financial and Corporate laws
7) Industry-specific laws
8) Advertising laws
9) Data privacy
10) Intellectual property rights
11) Foreign Exchange laws
As per the Companies Act 2013, Directors should certify in their annual Director’s Report how they have devised proper and effective systems for ensuring compliance with applicable laws. The report should also clarify if the systems were successful in operation.
Thus, all Indian companies need professionals who can bring about statutory compliance in HR to comply with the ever-changing environment of regulations.
Get a Free Demo Documents of The Minimum Wages Act 1948
Benefits of Statutory Compliance in HR for a Company
A company will save itself from the majority of serious legal troubles if it is statutorily compliant. This will also lead to the company’s sustained growth, as when the employees get treated well, they work with more ownership. The following are some of the benefits of statutory compliance for a company:
1. Improved business opportunities
If a company invests in significant compliance management systems, it can easily promote and preserve its goodwill. Due to this, the company can get a higher bargaining position during negotiations, and thus, it can secure much-needed business contracts. Also, companies that invest in advanced compliance regimes can attract more investments for improving opportunities and business prospects.
2. Higher employee retention
If a company has statutory compliance in the HR department, the employees are assured that they will get a professional, fair, and safe working environment. Statutory compliance in the HR department indicates that the company will provide a just and employee-friendly working environment and the company can resolve any law issues related to labor or employment. A company must comply with all its labor and employment law requirements to instill confidence among its employees that it cares about their welfare and well-being. This will blossom a healthy work environment resulting in enthusiastic and satisfied employees. Such employees are highly likely to stay with the company, making the rate of employee retention higher.
3. Prevention of legal penalties
Compliance with necessary statutory requirements will help a company to prevent the inevitable consequences of non-compliance like lawsuits, work stoppages, revocation or suspension of licenses, disqualification of its officers or directors, payment of penalties, imprisonment of officers or directors, and complete shutdown.
4. Improvement in quality
If a company adheres to statutory compliance, it will eventually improve the quality of its products and services. Statutory compliance will enable the company to focus on its main business activities instead of unnecessarily spending resources and time on paying penalties, effecting the compounding of offenses, penal liabilities against its officers or directors, retaining valuable and talented employees, or defending imprisonment or litigation. With statutory compliance, a company can prevent apparent risks that can emerge due to non-compliance. It will help the company to detect or avoid failures at the early stages. All of this will lead to greater efficiency in business operations.
5. Improvement in business operations
After a company successfully complies with all the applicable statutory compliance requirements, it frees up resources and time for focusing on its core business activities and R&D, paving the path to improved business operations. With secure business operations, the company achieves fabulous growth in its business.
6. Brand loyalty
A company’s principal investors and stakeholders will be assured that it places statutory compliance as one of its top priorities if the company has efficient compliance management programs and tools for achieving compliance with essential statutory requirements. The proper agreement reflects a company’s awareness, expertise regarding relevant regulatory mandates, and commitment to high ethical standards. It shows that the company intends to operate its business fairly and transparently. As a result, the employees, vendors, and customers begin to trust the company more, eventually strengthening brand equity and loyalty.
7. Boosting employee morale
If a company observes statutory compliance, it significantly boosts its goodwill and likable reputation. Such a company succeeds in positively influencing the performance of its employees. Non-compliant companies are unable to prove their commitment to proper business ethics.
Principled and talented employees are highly attracted to fully compliant companies. These companies can effortlessly boost employee morale, leading to better productivity, lower attrition rates, and improved business efficiency.
8. Improved public relations
A company will benefit from better public relations if it is fully compliant. Statutory compliance in the HR department of a company assures the company’s customers, employees, stakeholders, and investors that the company will always stick to highly ethical business practices.
9. Risk management
Every organization faces significant risks related to strategy, finance, operation, process and reputation, and compliance. Finance and Healthcare are highly regulated industries, and they usually face compliance risks which tend to increase when such companies begin their international operations. A company can prevent several legal troubles if it requires statutory compliance requirements. Statutory compliance will help companies to avoid as well as manage compliance risks.
10. Competitive differentiation
Statutory compliance in HR department of a company will prove to be a competitive advantage over rival businesses. Also, it will help the company to produce more excellent outputs and reduce compliance-related risks.
Benefits of Statutory Compliance in HR for Employees
When a company executes statutory compliance in HR, its employees get better treatment and sufficient benefits. The following are the benefits of statutory compliance in HR for employees:
1. The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
Employers provide bonuses to their employees under the Payment of Bonus Act. Mostly establishments and factories with 20 or more employees provide a bonus calculated based on the profits of the establishment and the employee’s salary. Also, if an employee completes 30 working days and draws ₹21,000 or less per month, he/she is eligible for the bonus payment in the ongoing financial year. The minimum rate of paying a bonus is 8.33% while the maximum rate is 20%. If any employee gets caught in any misconduct or fraud, he/she can get disqualified from bonus payments.
2. PF (Provident Funds)
Both Provident Funds and HR compliance are significant parts of each other. Provident Fund consists of the money saved throughout an employee’s working years. Provision of the Provident Fund ensures income when the employee retires. Unfortunately, if an employee meets early death, the PF gets passed on to his/her family.
3. TDS (Tax Deduction at Source)
When an individual receives a payment, his/her TDS gets deducted under the Income Tax Act. The CBDT (Central Board of Direct Taxes) manages this deduction. After filing the TDS return, the income tax department deducts the tax calculated from the income. The final amount is further repayment. The following are the cases in which TDS is exempted:
- When the Assessing Officer provides a certificate of exemption
- When the receiver provides a self-declaration that states that he/she has mentioned the required investments in FORM 15G/15H
The following elements are Also Impact the TDS deductions:
1. Medical allowance
2. Education
3. Investments
4. Travel leave
4. Professional Tax
The State Government levies the professional tax on every person who earns a living through any medium. This tax, as well as its calculation, varies from state to state. The professional tax is deducted based on the state-declared slab. A few states and union territories in India do not charge professional tax. The annual professional tax gets divided into 12 equal installments that must be paid monthly. However, the professional tax in February is higher than in the other months.
Statutory Compliance is Applicable to
1. The companies in India may take the following steps to ensure statutory compliance in HR:
2. Educate professionals about applicable statutory, legal, and regulatory compliance requirements.
3. Identify the suitable business spots whose statutory and legal landscapes are required to comply with.
4. Each business location (including international branches) should have statutory compliance requirements.
5. Compliance responsibilities should get laid to specific departments or personnel.
6. Compliance review should get conducted to identify gaps in compliance.
Challenges in Statutory Compliances in HR
The companies in India face the following challenges in statutory compliance in HR:
1. Lack of awareness
It is standard for a company’s professionals to lack expertise and adequate knowledge of statutory compliance requirements. When such a company has multiple locations internationally, its compliance risk increases; therefore, a company must have professionals with proper experience in statutory compliance for a smoother running of the business.
2. Segmented compliance initiatives
In most companies, several departments control various functional activities of the business. Such companies can’t ensure effective compliance in their companies.
3. Dynamic statutory landscape
Statutory requirements continuously evolve and emerge with complexities, making it difficult for companies to keep up with the dynamic statutory landscape.
Companies who spend enough resources on statutory compliance requirements in HR will find the investment worth it as they will get numerous benefits from it and the protection against non-compliant issues. Before joining a company, an employee should also check whether it is statutory compliant. All the companies in India must carry out statutory compliance in HR to ensure a professional and employee-friendly working environment.
Join a Community of 1,00,000+ HR Professionals